What is Buckling?
Buckling is an important concept in engineering, which is used to predict the behaviour of structures under a certain load. The buckling load refers to the amount of load required before a structural member or whole structure begins to buckle, meaning it will fail. When a structure is at its buckling point, the forces are just enough to cause structural failure. Buckling is typically sudden and irreversible. A more complicated way that engineers often use for discussing buckling loads is by using the concept of critical loading factor (CFF). This number expresses how much force must be applied in order to reach a certain load percentage in comparison with the original maximum load
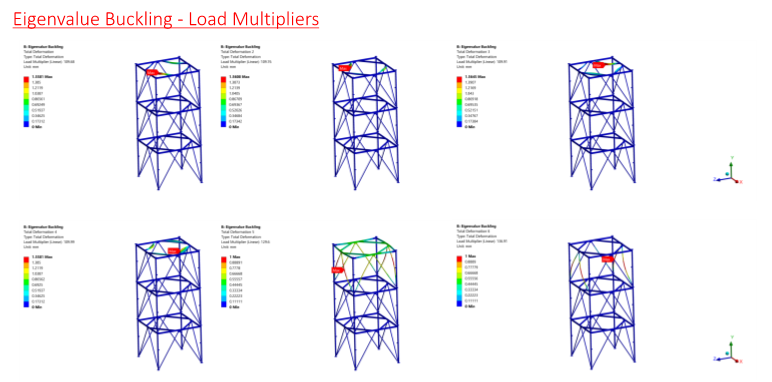
It is based on FEA (Finite Element Analysis) and Non-linear analysis, which are used to calculate the Load Multiplier. This multiplier determines how much load a structure can withstand before it buckles.
Linear vs. Non-linear Buckling:
Linear and Non-linear Buckling analysis are two of the most important methods used in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). Linear buckling analysis is used to study the stability of a structure under various load conditions. The load multiplier is an important parameter that is used to determine the amount of load a structure can withstand before it buckles. On the other hand, non-linear buckling analysis takes into account the non-linear behaviour of the material under different loading conditions. Under this approach, the shape of the beam will be determined by the deformation in different real parts of the beam due to loading conditions. The linear buckling analysis can be performed when a cross-section is under uniform load on a straight axis. The non-linear buckling analysis must also consider not just one cross-section but many of them to ensure that they are all under different loading conditions.
A real-life case study for Buckling analysis:
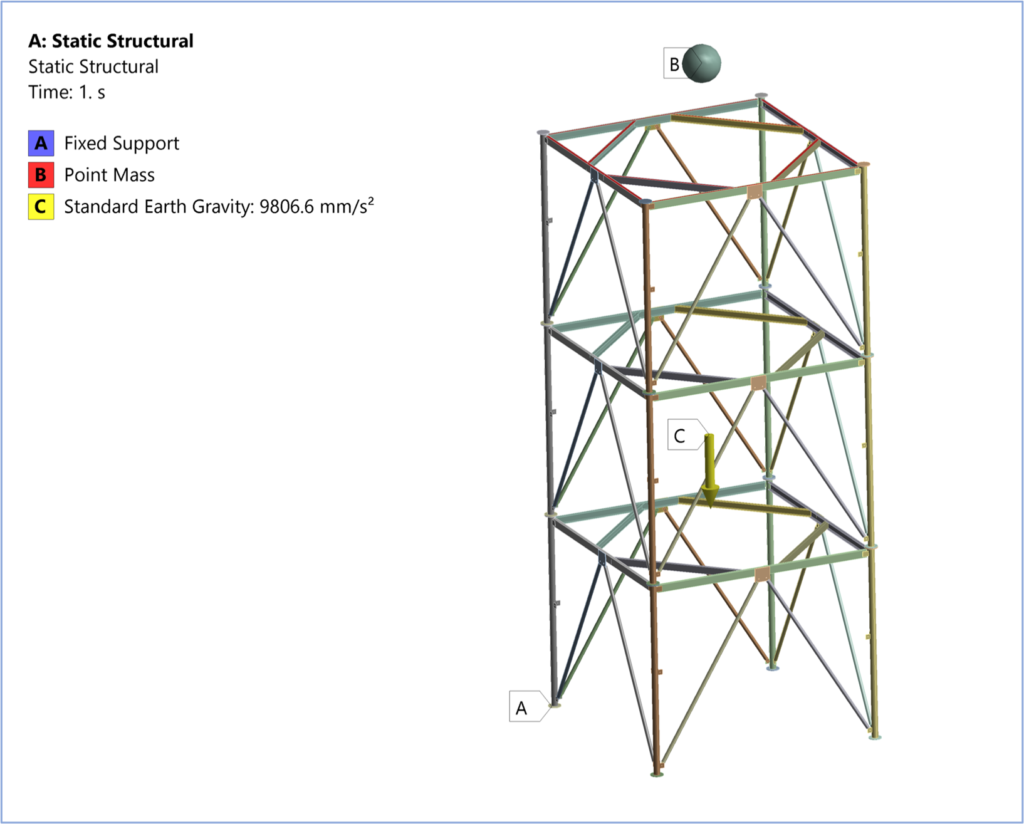
X band weather radars are used for in-land weather monitoring. The radar enclosure houses a complex electronics instrument and mounted on a structural platform at 150 ft from ground level. The structure is subjected to very high wind and seismic zones. And due to high self-weight of the radar, the structure is prone to buckling failure.
FEA buckling analysis is performed to check the structural integrity for the following conditions –
- DL
+ Equipment Load
- DL + WL (Wind Load)
- DL + Seismic load
Conclusion:
In conclusion, non-linear buckling analysis in FEA is a powerful tool that can help predict the behaviour of structures under external loading conditions. This analysis can provide valuable insights into the critical loads and modes of failure of structures by accounting for geometric and material non-linearities.
Graphler Technology is one of the leading product design companies in India. We have experts in FEA services and also we are specialized in CAD Conversion Services, 2D to 3D Conversion services, engineering animation services etc.

